Research Projects Supported by
HKU's High Performance Computing Facilities
¡@ |
|
Researcher: |
|
Professor S T Tan, Department of
Mechanical Engineering |
|
|
Project Title: |
| Heterogeneous Solid Modeling Using Materially Defined Geometric Entities |
|
|
Project
Description: |
It is known that components
designed with heterogeneous materials show key advantages over those
designed with a homogeneous material as anisotropic and/or other desired
properties of the materials can be incorporated. Traditional limitations due
to material incompatibility (e.g. stress concentration and non-uniform
thermal expansion) have been overcome by incorporating gradual material
variation in the designed component. Arising from this, many engineering
studies have focused on heterogeneous solid modeling in recent years.
This project aims to extend and enhance the traditional homogeneous solid
modeling methods by incorporating material information in the 1D, 2D and 3D
geometric entities. Such a representation guarantees a more flexible
material variation to be defined throughout the 3D space and the user¡¦s
design intent can be intuitively captured. Moreover, a range of
heterogeneous objects which are difficult or unable to be defined with
existing methods can be represented.
¡@ |
|
Project Duration: |
|
Three Years |
|
-
Back to top- / Contents |
|
|
Project
Significance: |
|
The outcome arising from
this project would be a software module built on top of the ACIS kernel,
which would allow heterogeneous components to be modeled. The representation
scheme would guarantee a more flexible material variation to be defined
throughout the 3D space and the user¡¦s design intent can be intuitively
captured. Moreover, a range of heterogeneous objects, which are difficult or
unable to be defined with existing methods, would be able to be modeled. An
example object is shown in Fig. 1. |
|
|
Results
Achieved: |
The long term impact of this
investigation of representation scheme is that it would provide a useful
platform for contemporary CAD systems to incorporate facilities for modeling
heterogeneous objects. This work would also provide great impetus for
research work on the fabrication of heterogeneous objects through
state-of-the-art LM technologies.
¡@ |
|
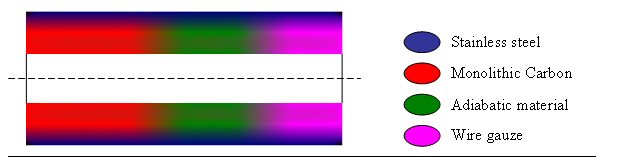
Fig.1 A section view of a
sorption tube in a refrigerating/heat-pump system (with material gradation) |
|
|
Remarks on the
Use of High Performance Computing Cluster: |
|
HPC Cluster would speed up the
computation of the materially defined points in the model. However, it would
be very expensive for the users in the industry to afford a HPC Cluster. |
|
|
Email Address: |
|
sttan@hku.hk |
|
|
-
Back to top- / Contents |
